AntiviralTex

Antiviral and antibacterial effect technology
Antiviraltex the first fabric capable of quickly destroying the virus.
Silver ions and fatty acid vesicles
Anti-viral articles contain silver ion components to deactivate and immobilise the virus, in addition to fatty acid vesicle technology that quickly destroys it by physical contact.
Untreated fabric
Fabrics are perfect breeding grounds for bacteria and viruses. Indeed, they may remain active on these surfaces for days and even months. Coronavirus can survive up to 2 days on room temperature surfaces.

AntiviralTex treated fabric
Antiviraltex contains silver ion components to deactivate and immobilise the virus, in addition to fatty acid vesicle technology that quickly destroys it by physical contact.
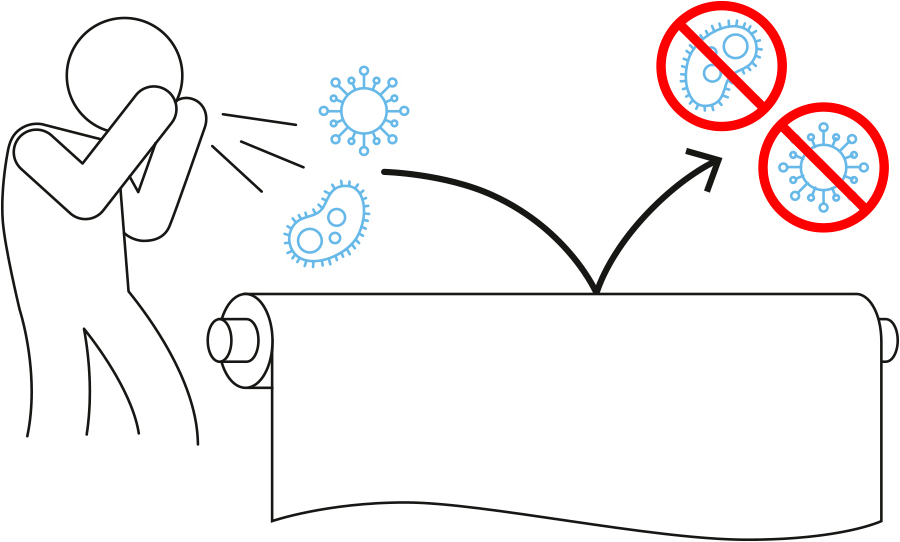
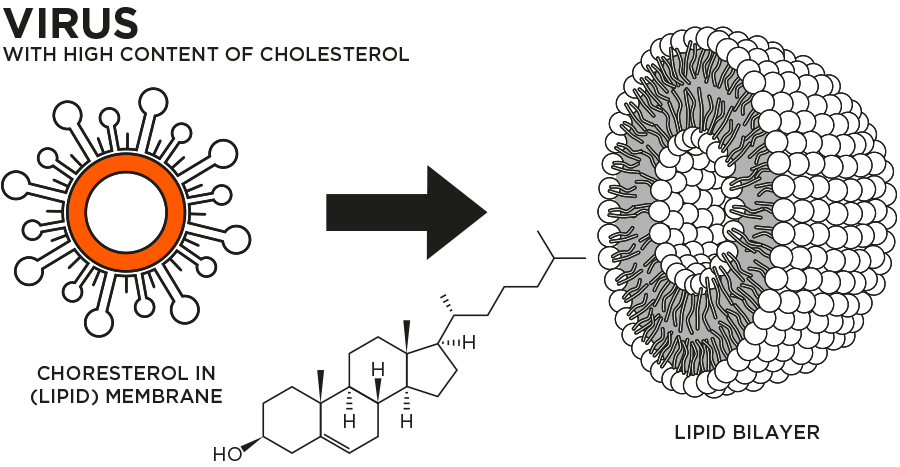
AntiviralTex functioning
1. Silver component attracts and deactivates the virus
- Silver ions attract the oppositely charged viruses and binds permanently to their sulphur groups.
- The virus is effectively immobilized and inactivated.
2. The virus is effectively immobilized and inactivated
- The fatty spherical vesicle technology functions by directly targeting the lipid envelope surrounding the virus.
- This technology helps detach the viral membrane from its cholesterol content, thus destroying the virus.
- Vesicle component destroys the virus.
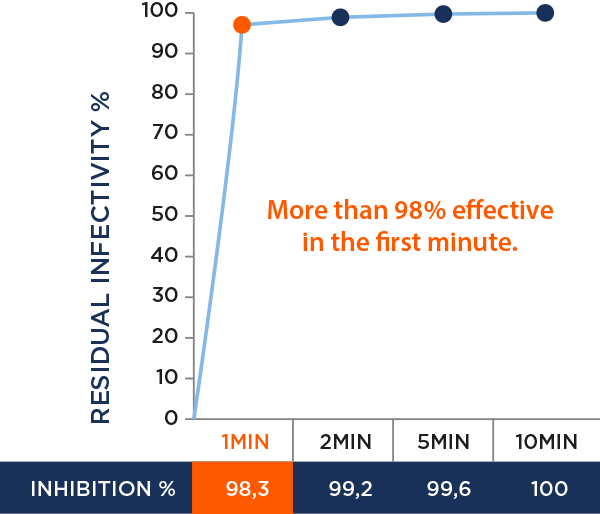
Rapid effect
Residual virus infectivity tested according to a modified ISO 20743 method (Sendai virus).
Rapid antiviral effect demonstrated within 2 to 5 minutes.
AntiviralTex is 100% effective in a few minutes.
Antiviral effect
This anti-viral fabric can withstand 30 to 90 washes at 40º (ISO 63304G), depending on use requirements.
ISO 18184:2019 compliant.
Products used in Antiviraltex articles meet BPR and UE REACH standards.
The Antiviral Testing has been prepared for “Textiles Rumbo, S.L.” in Laboratory “Situ Biosciences LLC” in the USA.
How does the ISO 18184 method evaluate the virucidal efficacy of a textile product?
The most common test conditions is within 2-hour exposure and incubation to the test substance of the inocula dose of the viral titer.